Abstract
Introduction and aim : Several clinical trials have shown that the incorporation of novel agents (i.e., proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib and immunomodulatory drugs, thalidomide and lenalidomide) in the treatment of newly diagnosed symptomatic multiple myeloma (MM) patients improves their time to first response and survival outcomes. Nevertheless, some patients still die within 3 months (early death, ED) from starting treatment. Thus, we investigated the effect of novel agents- containing first line treatments on the risk of ED of MM patients.
Study design : retrospective analysis of a cohort of 991 newly diagnosed symptomatic MM patients consecutively treated at a single Institution from 1997 until 2015 at the Hematology Division of the Ospedale Papa Giovanni XXIII (formerly, Ospedali Riuniti) of Bergamo, Italy.
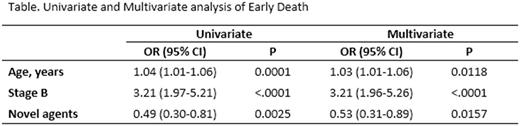
Results : during the entire period of analysis (18 years), 708 patients (71.4%) died. They were 374 men and 334 women, aged 25-94 years (median 68 years). Types of MM were: IgG (n=357), IgA (n=138), light chain (n=125), plasmacytoma (n=23), non-secretory (n=16), plasma cell leukemia (n=11), IgD (n=6), IgM (n=4), unknown (n=28). Durie and Salmon clinical stages were: I (n=75), II (n=111), III (n=479), unknown (n=43). A/B stages were: A (n=518, 73%), B (n=147, 21%), unknown (n=43, 2%). Treatments were as follows: conventional chemotherapy (CC) (n=255, 36%), CC + autotransplantation (ASCT) (n=150, 21%), novel agents (n=181, 26%), novel agents + ASCT (n=122, 17%). Ninety-two patients (9.3%) experienced an early death (ED cohort) and the other 616 patients died > 90 days from starting treatment (late death, LD, cohort) (91.7%). Univariate and multivariate analysis (Table) showed that patients in the ED cohort were significantly older and had more commonly stage B MM compared to patients in the LD cohort. Incorporation of at least a novel agent in the first line treatment resulted in a significant reduction of ED. This beneficial effect was only seen in patients not enrolled in ASCT programs (p<0.001, Odds Ratio, OR, 0.37, 95% Confidence Interval, CI, 0.20-0.69 and p=0.009, OR 0.42, 95%CI 0.22-0.81, by univariate and multivariate analysis, respectively). Progression of MM was the cause of all ED events. Only one patient in the ED cohort started a second line of treatment.
Conclusions : Administration of first line regimens containing at least a novel agent significantly reduced the ED rate of patients with MM. Particularly, this improved survival was beneficial in patients not enrolled in ASCT programs.
Rambaldi: Novartis, Amgen, Celgene, Sanofi: Other: Travel, Accomodations, Expenses; Novartis, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, Italfarmaco: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal